UP TO THE MINUTE
Low-cost Methods for Strengthening Your Old Metal Roof

By Dale Nelson, Roof Hugger, LLC.
If you’ve been searching for an affordable solution for your metal roof, look no further.
Natural disasters are a common occurrence, and they seem more powerful than they’ve ever been. This means it’s more important than ever to have a sturdy, reliable roof to keep you safe no matter what Mother Nature sends your way. Luckily, modern technological improvements and stricter building codes have made it so that today’s buildings are studier than yesterday's. However, this doesn’t mean older buildings are as fully protected as they could be. If you want to improve your roof's chance of weathering the storm, there are some low-cost methods for doing so.
Prior to 2000 and the adoption of the International Building Code (IBC) building roofs were designed based on uniform or equal loading across the entire roof. For example, an 80 wide x 100 long x 22 eave height building, in Tampa, Florida, would have a wind speed design of 110 mph and loading of about -20 lbs./ psf. over the whole roof. After 2000 and the more universal adoption of ASCE-7 and the IBC code, roofs were more accurately divided into “zones.” (I) Roof field, (II) edge zones and (III) corner zones were created. The latest version of the 2021 IBC code has added even more roof zones.
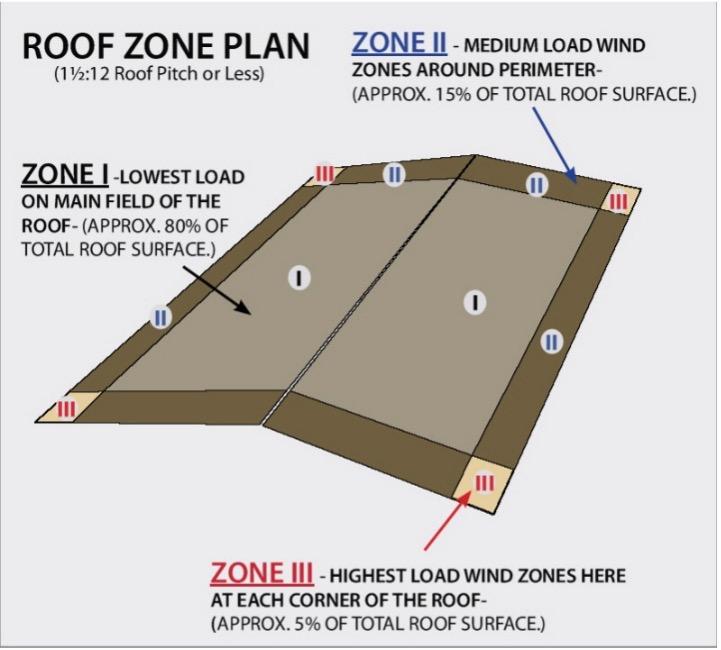
Each zone has its own design loading for uplift; the corners would be the highest loading, edges next highest and field the lowest. That same 80 x 100 x 22 building in 2022 now uses 141 mph wind speed, roof loads are now -34psf in the field, -45psf in the edges and -62psf in the corners. 3x the original design. If this building was in an open terrain area, the corner zone loads would increase to over -80psf. This is four times the original load design of older buildings.
The good news is that it is possible to retrofit almost any older building and bring it to the current IBC design requirements. Like all re-roofing however, retrofitting can be expensive.
Metal roofing is a premium long-life product, so what if your old metal roof is still in ok shape and you can’t afford a retrofit roof? There are a few things you can do to make your existing roof stronger, giving your building and its contents a better chance of surviving an extreme storm event.
Will these changes allow you to meet the current code? Probably not, but your old code roof will certainly be stronger than it is currently.
Many older roofs are the through-fastened or screw-down type roofs. First, inspect the old fasteners, replace any corroded or loose fasteners with quality, oversize stainless steel or zinc alloy, weather guard fasteners – these small fasteners are a critical part of your building. They not only hold your roof down to the structure, but they transfer the diaphragm strength of the roof panels to the roof framing giving it needed structural rigidity.
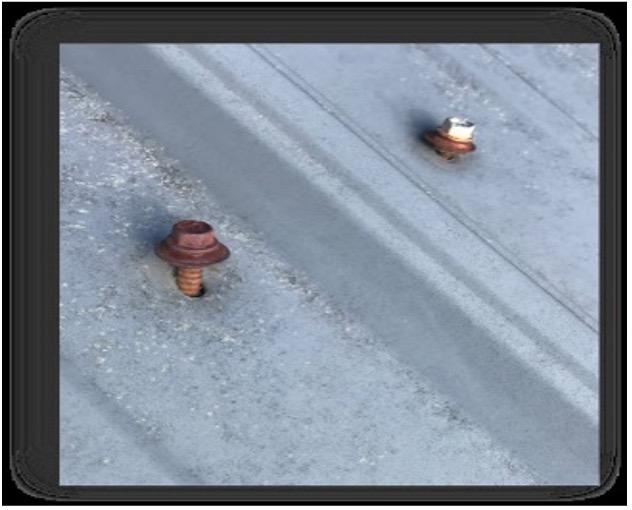

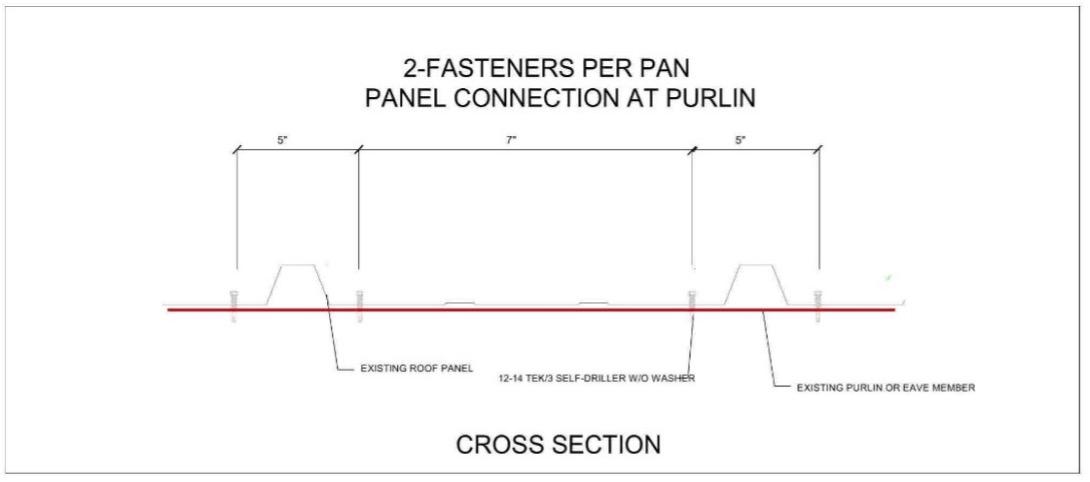
The most common metal roof panel is the 12” o.c. ribbed “PBR” panels. These panels are typically attached with 1-fastener every 12”.
It’s hard to believe but just adding just 1 additional fastener to the panel every 12” for a total of 2 fasteners per L.F. in zones II & III, (Typically 5’-10’ in from the eave and rake of the building) will increase the strength dramatically. The design capacity of a typical “R” panel in these areas could increase from approximately -45lbs/psf to around -60lbs/psf. Assuming 5’ purlin spacing this one additional fastener can improve roof panel design capacity by 33% or more. It is also important to note this increase is in design capacity. Metal roof panel design capacity is typically decided after a factor of safety of 2.0 is applied. Theoretically, this means they should have even more capacity before predicted failure.
The next thing to look at is the buildings rake trim. That is the trim piece on the gable end of the building at the top of the end. It covers the side edges of the roof panels.
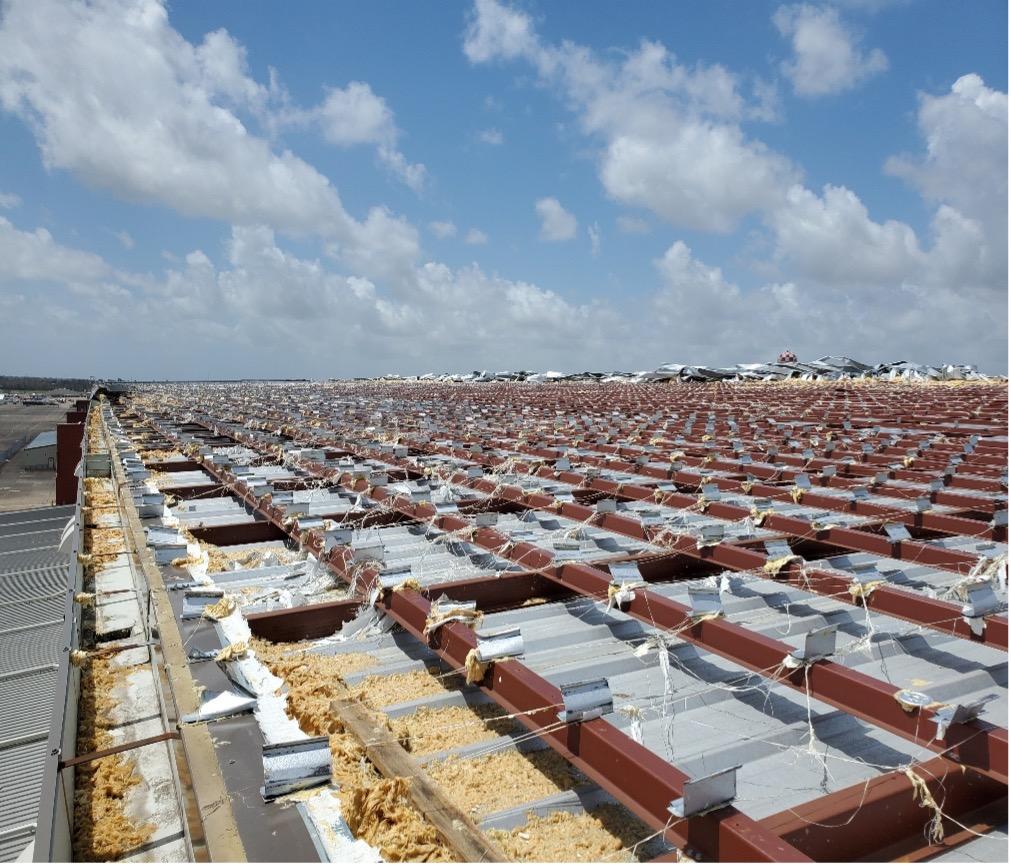

Most roof failures begin at the corners or rake edges of the building. If the trim comes off, the edges of the panels become exposed to the harsh pressure of the wind. This applies to the wall corner trim as well. I prefer these trim fasteners to be no more than 12” o.c.
Finally check the gutter attachment and make sure the straps and attachment fasteners are not corroded and weak, replace them as needed. They are typically spaced about 3’-0” o.c.
OK, but what can you do if you have a standing seam roof, not a screw down roof? Adding fasteners to a standing seam roof defeats the whole reason to have one because standing seam roof panels need to be allowed to move with expansion and contraction. High strength sliding clips are seamed into the roof panel side-laps and have the ability to hold the panels firmly down and still slide as the panels move with heating and cooling.
The capacity of these panels is in large part controlled by the clips that hold the panels. A common mode of failure is the panels detaching from the panel clips. It is possible however to increase the holding power of these floating clips by adding external “Wind Clamps” or “External Seam Clamps.” These clamps are installed on top of the roof panel seams at the attachment clips. The clamps do not penetrate the panels nor do they impede the movement of the panel, but they greatly increase the holding power of the panel to the clips.
A typical 24” standing seam panel on 5’ purlins may have a design capacity of -35 to -40lbs/psf. Adding wind clamps may increase that capacity to -60lbs/psf or more. Like other metal panel roofs, you would want wind clamps in zones II & III. Many of these type remedies are also allowable for FM insured under their loss prevention data sheet #1-31 2.2.2.2 B for use of External Seam Clamps (ESC).

Once again this will probably not get you to the current requirements in high wind coastal areas, but you might be close in the Midwest and West. A local engineer can easily check this if you wish.
No doubt a new full, code compliant, roof retrofit is the best way to “harden” your existing building to meet the current wind and/or snow load requirements. It will also provide a dependable, energy efficient, 60 year or more life roof making this the lowest life-cycle cost roof system available. At Roof Hugger, we look forward to working with you when you are ready for that new roof.


In the meantime, it is great to know you can do a few things to measurably strengthen the roof you have and do it on a limited budget.
Learn more about Roof Hugger in their RoofersCoffeeShop Directory or visit roofhugger.com.
Original article source: Roof Hugger
Recommended For You

EagleView Launches EagleView Developer
Read More ...
Optimizing your home’s airflow
Read More ...
Beauty and strength: The best of both worlds
Read More ...














Comments
Leave a Reply
Have an account? Login to leave a comment!
Sign In